|
When a system is in dynamic equilibrium, the system remains stable within fluctuating limits.
An example of dynamic equilibrium is your body. There are many systems in your body that maintain equilibrium, such as, the nervous system, digestive system, circulatory system, endocrine system, excretory system, and skeletal muscles.
All homeostatic control systems have three funtional components:
- monitor
- coordinating centre
- regulator
Pattern of Homeostasis
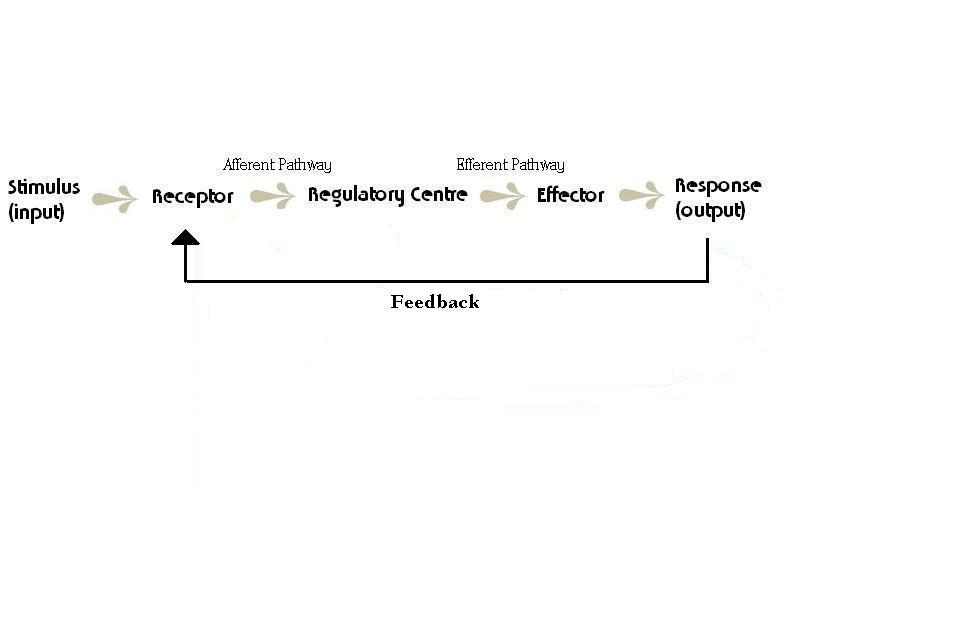 There are two types of feedbacks in homeostasis. There is a negative feedback and a positive feedback.
- negative feedback: is a process which slows down or stops a reaction, reducing the stimulus or its effects; maintains equilibrium
- positive feedback: is a process which emphasizes or increases a response to a stimulus; serves to destroy equilibrium
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the maintenance of body temperature within a range that enables cells to function efficiently.
Invertebrates, most fish, amphibians, and reptiles are referred to as ectotherms or poikilothermic because they depend on the surroundings to regulate metabolic rates. Mammals and birds are referred to as endotherms or homeothermic because they are able to maintain a constant body temperature despite the surroundings.
Stimulus-Response in Thermoregulation
|
Stimulus
|
Response |
Effect |
|
Decreased environmental temperature
|
· Constriction of blood vessels in skin
· Hairs on body erect
· Shivering rhythmic contraction of skeletal muscle |
· Limits blood flow, which reduces heat loss from the skin and retains heat in the core of the body
· Traps warm air to the surface of the skin to reduce heat loss; Goosebumps are made by the contraction of the muscle attached to the hair
· Generates heat production by increasing metabolism
|
|
Increased environmental temperature |
· Dilation of blood vessels of skin
· Sweating |
· Allows more blood flow to the skin blood loses heat to the skin
· Evaporation of perspiration from the skin causes cooling |
|